Plastics
Polystyrene (PS)
General information
Description
Polystyrene (PS) is one of the most inexpensive and widely used plastics. It is a hard, transparent, and brittle thermoplastic with a low impact resistance. HIPS (high impact polystyrene) is a modified form of PS with higher impact resistance. HIPS is not transparent. Both PS and HIPS can have a high gloss. Characteristic for rigid PS is the tinny sound it makes when tapped upon while PS foam often makes a squeaky sound.History
Polystyrene was patented in 1929 and became commercially available in 1931. PS foam has been produced since 1944. From 1949 onwards the well-known Styrofoam with its spherical structure has been produced.Production, Application, Appearance
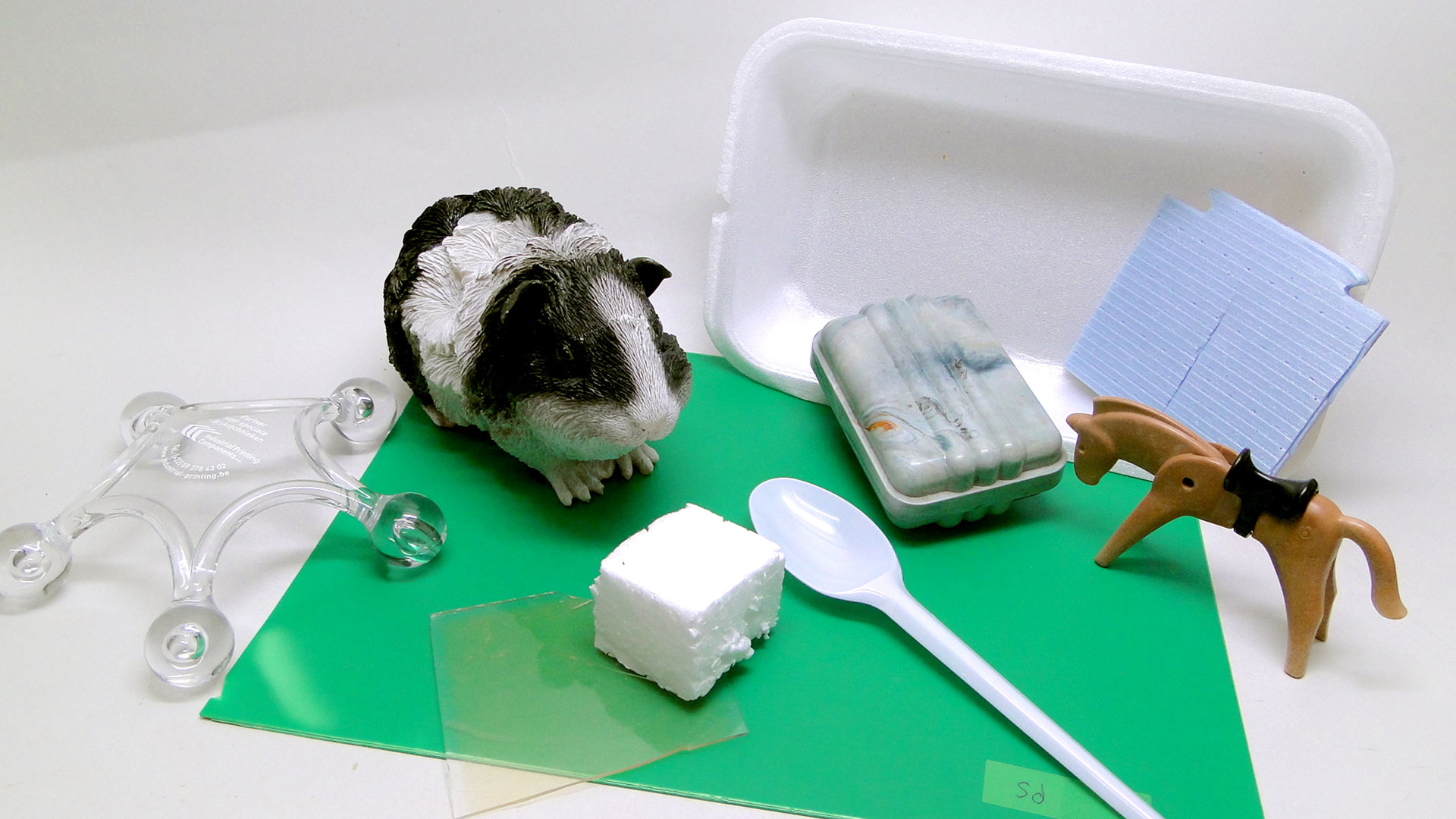
Polystyrene can be processed in different ways. The pellets are usually heated and extruded into sheet or film, injection moulded or thermoformed (vacuum formed). It can be foamed with blowing agents. PS is used for many purposes, from disposables to design objects. For example disposable cutlery, inexpensive toys, (food) packaging, and TV casings.Properties
Material properties
ThermoplasticDensity: Rigid = 1.04-1.06 g/cm3; EPS foam = 0.015-0.040 g/cm3; XPS foam = 0.028-0.045 g/cm3
Melting point: 275°C
Glass transition temperature: 85-102°C
Identification properties
Cell structure (foam): closed or sphericalSmell: no characteristic smell
Touch: no characteristic touch
Sound: Rigid = tinny; foam = squeaky; film = no characteristic sound
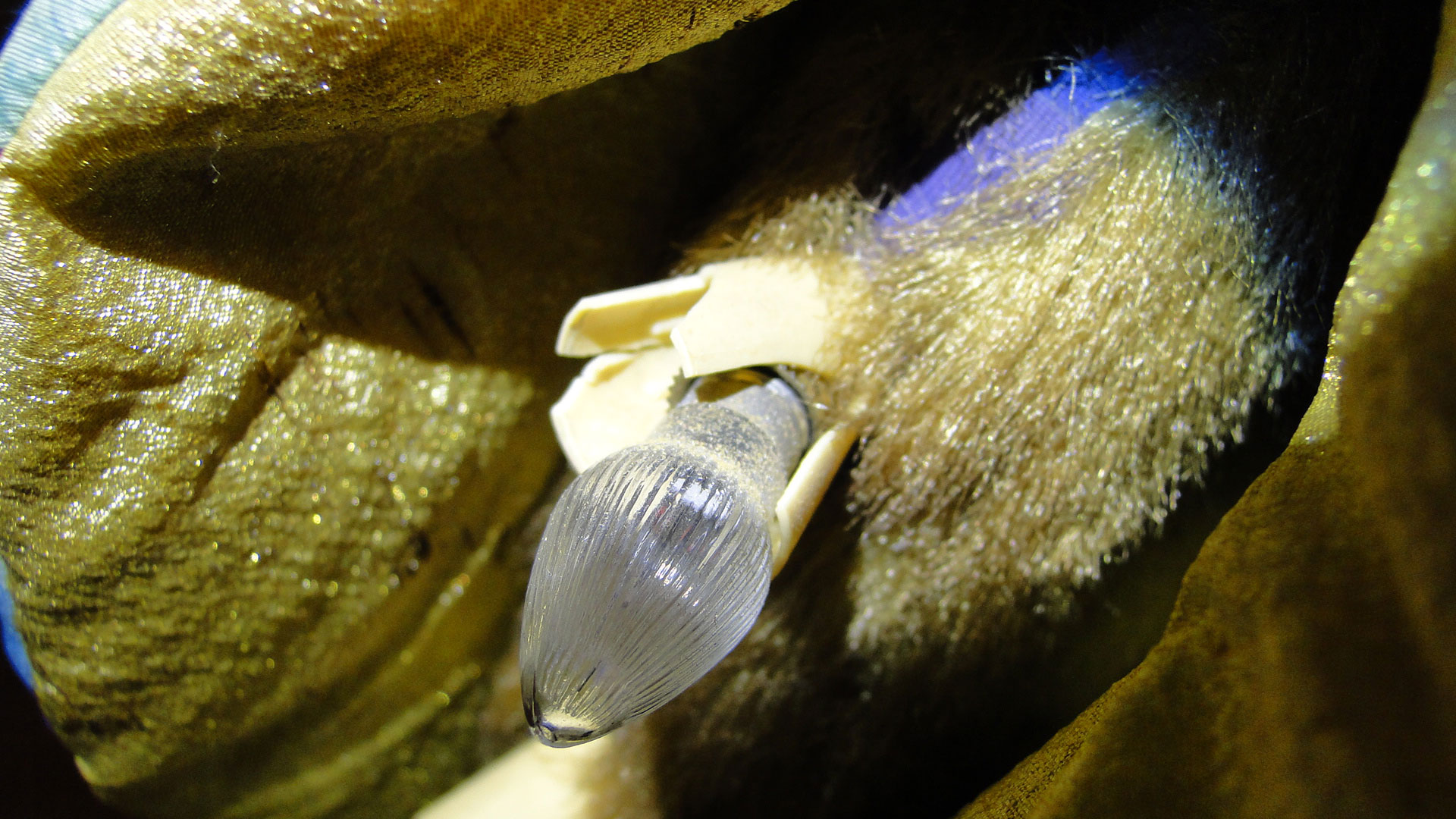
UV-radiation (when clear): fluoresces blue
Polarizing filters (for clear PS): does not produce a colour pattern
Degradation
Process
Photo-oxidation; absorption of moisture.Details
PS is not considered a problem plastic.Symptoms
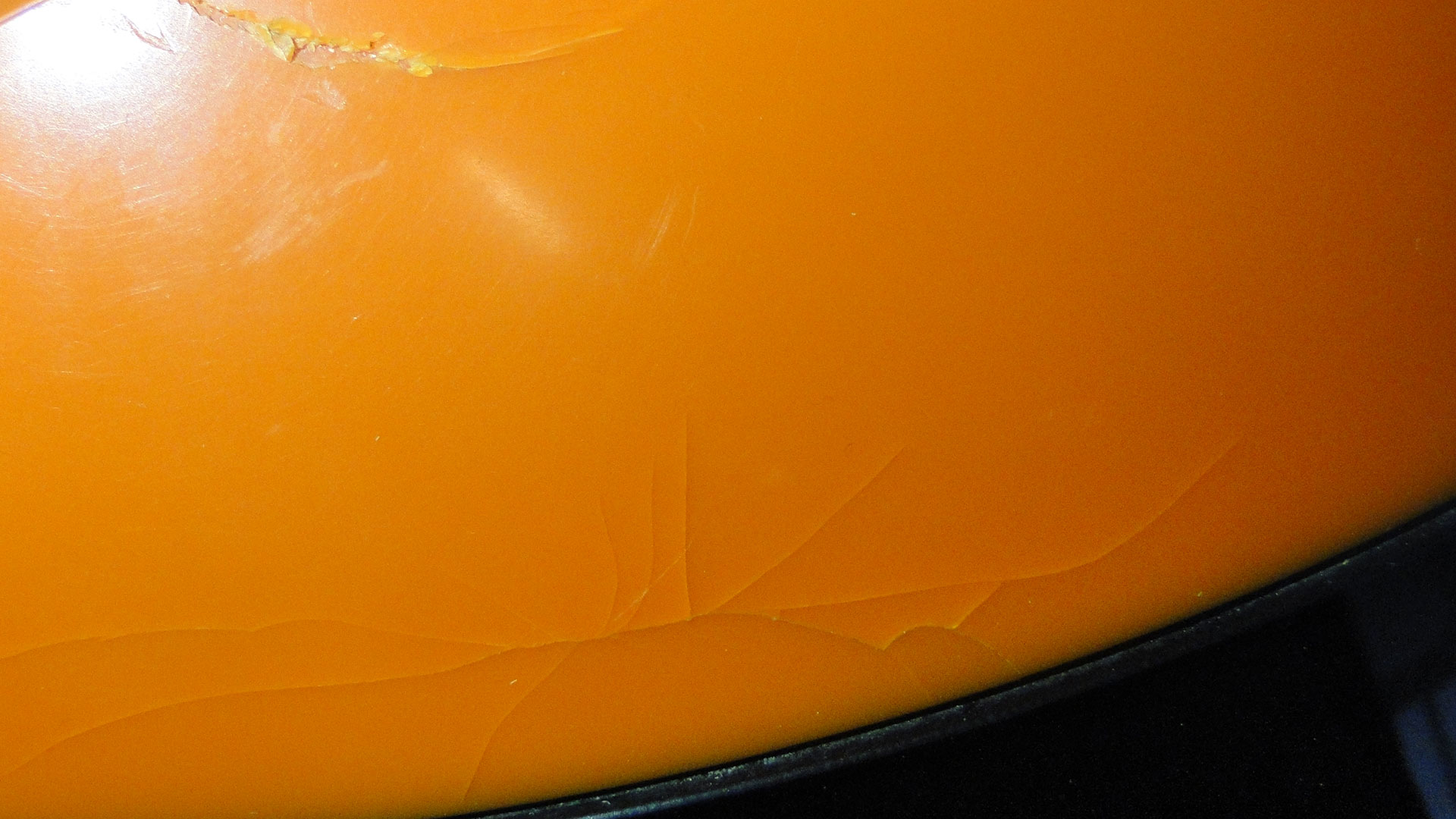
Yellowing, surface turns matte, loss of mechanical properties resulting in tears and fractures.Susceptibility
UV-radiation: HighLight: Medium
Oxygen/Ozone: Low
Temp: High - becomes brittle below 0°C
RH: High - RH fluctuations
PS is highly susceptible for polar and non-polar solvents, especially acetone; also for plasticizers that can be emitted by other plastics.
Preventive conservation
Recommendations
UV-RADIATION: keep below 10 µW/lm Exclude UV with filters or no-UV light sourceLIGHT: 1 slight change in approx. 30 Mlx.h Moderate light dose - control intensity and exposure time
OXYGEN / OZONE: ambient conditions
TEMP: Do not keep below 0°C
RH setpoint: common indoor conditions 30-70% RH fluctuations: keep constant - setpoint ±5%
For EPS: handle with care - it is not elastic and indentations are irreversible
Other names
- Styrofoam
- Polystyrol
- Arrasol
- Piepschuim
- Styropor
- Tempex
- Depron