Plastics
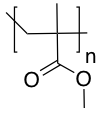
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)
General information
Description
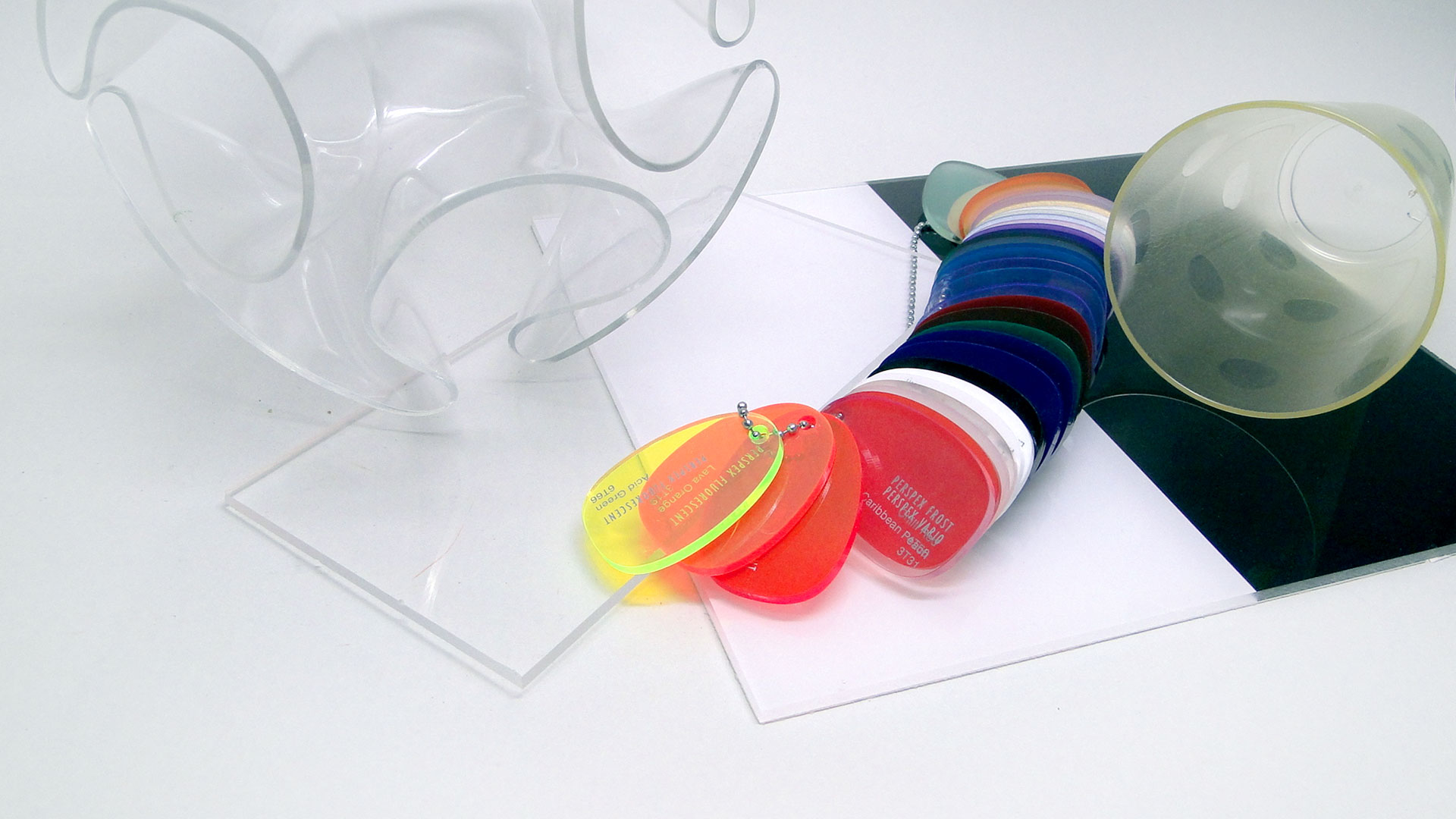
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is a clear transparent thermoplastic which is often used in sheet form as a light-weight alternative to glass. PMMA can be produced in different colours, translucent and opaque. The surface can be polished to obtain a high gloss. However, it scratches easily.History
The polymerisation reaction of methyl methacrylate was discovered in 1877. In 1933 the polymer was patented and registered in Germany as Plexiglas. At about the same time it was registered in England under the tradename Perspex while in the US it appeared under the trademark Lucite. In 1936 commercial production of acrylic safety glass started.Production, Application, Appearance
PMMA is processed in different ways. It is well known as sheet but can also be cast in a mould or used for injection-moulding. Sometimes calcium carbonate or fibreglass are added to PMMA. Apart from being a substitute for glass, PMMA is used in jewellery, fashion accessories, furniture, kitchen utensils, and other design items.Properties
Material properties
ThermoplasticDensity: Rigid = 1.17-1.20 g/cm3
Melting point: 105-160°C
Glass transition temperature: calc.=82-105°C; exp.=104-105°C; atactic=105-122°C; isotactic=51-107°C; syndiotactic=105-120°C
Identification properties
Cell structure (foam): not applicableSmell: no characteritic smell
Touch: no characteristic touch
Sound: Rigid = no characteristic sound
UV-radiation (when clear): does not fluoresce. Sometimes faint
blueish fluorescence
Polarizing filters (for clear CE): does not produce a colour pattern
Degradation
Process
Photo-oxidation: random splitting of polymer chain which may be accompanied by emission of gases such as methane, hydrogen gas, carbon monoxide and dioxide, methyl formate, methyl methacrylate, and methanol. PMMA is hygroscopic, absorbs and desorbs moisture which can cause crazing.Details
NoneSymptoms
Surface becomes matte, decrease of transparancy (milky clouds). A typical degradation phenomenon for PMMA is the formation of small cracks and fractures on or below the surface (crazing).Susceptibility
UV-radiation: LowLight: Low
Oxygen/Ozone: Low
Temp: High - becomes brittle at low temperatures
RH: High - crazes with fluctuating RH
PMMA is sensitive to solvents.
Preventive conservation
Recommendations
UV-RADIATION: avoid extremesLIGHT: 1 slight change in approx. 300 Mlx.h Avoid high light dose
OXYGEN / OZONE: ambient conditions
TEMP: do not keep below 0°C
RH: setpoint 30-70% RH fluctuations: keep constant - setpoint ±5%
Other names
- Perspex
- Plexiglas
- Acrylate
- Acryl
- Lucite
- Acrylite