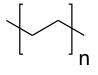
Plastics
cross-linked polyethylene (PE cross-link)
General information
Description
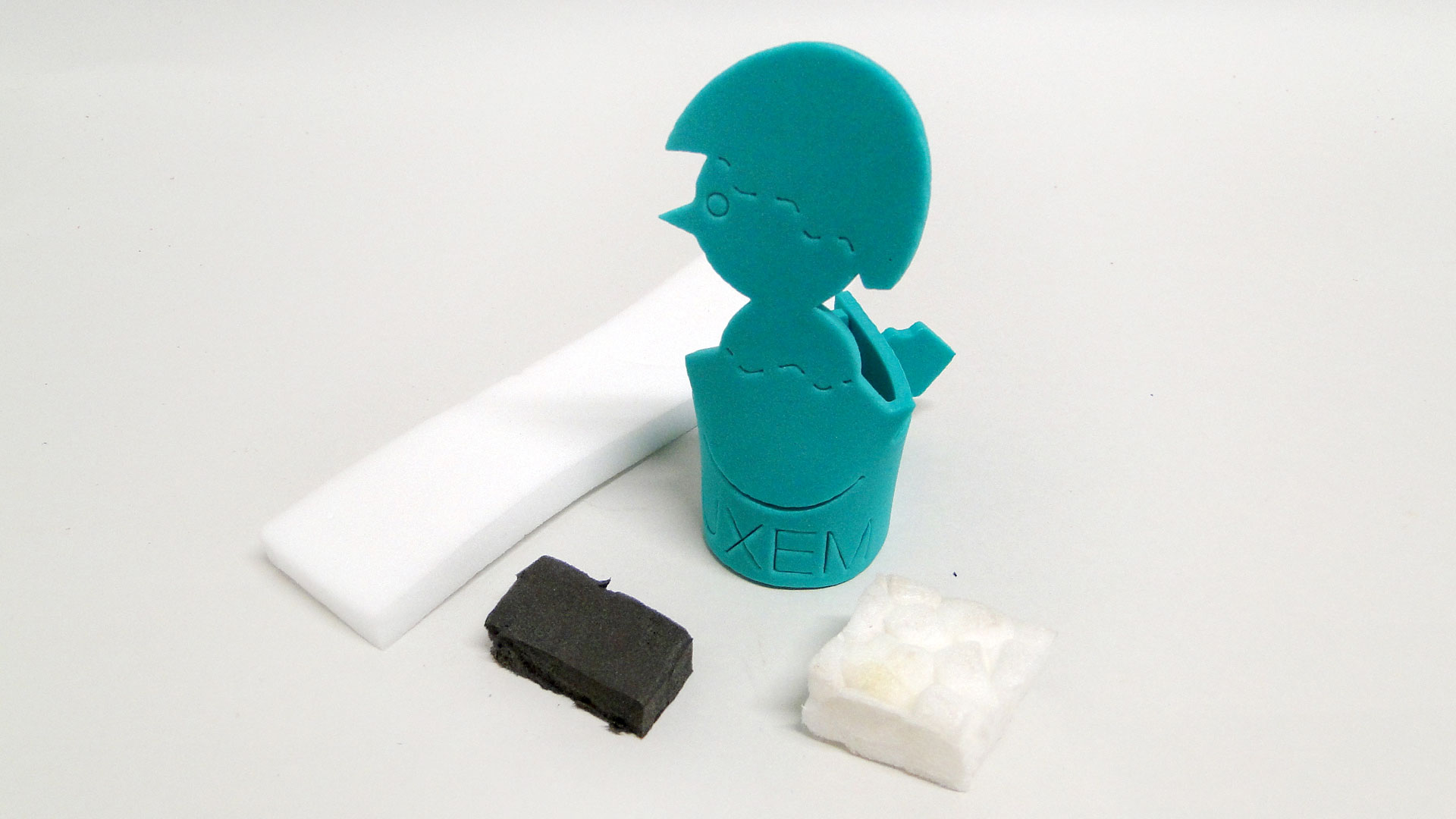
Cross-linked Polyethylene only exists as foam. It is produced as blocks and sheets or can be injection-moulded. It has a compact, closed cell structure with small cells. It is a semi-rigid foam that feels soft but cannot be pushed in easily. Cross-linked PE and EVA foam look quite similar (EVA is a co-polymer with a high PE content). They can be distinguished by touch: cross-linked PE feels more waxy while EVA feels more velvety. PE foam can develop a smell of old Tupperware or old plastic bags.History
PE foams became commercially available after World War II.Production, Application, Appearance
Cross-linked Polyethylene has better physical and chemical properties than non-cross-linked PE. Hence it is more expensive. Usually cross-linked PE foam is available in sheets of 0.3-10 cm thickness. It can be used for insulation, packaging, medical applications, and sports mats.Properties
Material properties
ThermoplasticDensity: foam: 0.015-0.2 g/cm3
Melting point: 99-138°C
Glass transition temperature: -59 to -133°C
Identification properties
Cell structure (foam): closedSmell: smell of old Tupperware or old plastic bags
Touch: waxy
Sound: foam = no characteristic sound
UV-radiation (when clear): not applicable
Polarizing filters (for clear EVA): not applicable
Degradation
Process
Photo-oxidation Soiling (electrostatic).Details
PE cross link is not considered a problem plastic.Symptoms
Discolouration, surface turns matte, loss of mechanical properties resulting in tears and fractures, dimensional changes.Susceptibility
UV-radiation: HighLight: Medium
Oxygen/Ozone: Medium
Temp: Low
RH: Low
Preventive conservation
Recommendations
UV-RADIATION: High l Light: Medium l Oxygen/Ozone: Medium l Temp: Low l RH: LowLIGHT: 1 just noticeable change in approx. 30 Mlx.h Moderate light dose - control intensity and exposure time
OXYGEN / OZONE: lower temperature slows down oxidation
TEMP: common indoor conditions 10-30°C
RH: common indoor conditions 30-70% RH fluctuations: setpoint ±20%
Am I dealing with...
TAGS
- Closed cell structure
- Fine cell structure
- Skin
- Hard
- Tupperware / plastic bags smell
- Waxy feeling